(U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) On April 2, 2018, the Administrator signed the Mid-term Evaluation Final Determination which finds that the model year 2022-2025 greenhouse gas standards are not appropriate in light of the record before EPA and, therefore, should be revised. The Federal Register Notice announcing the Administrator’s decision is available for review below.
Federal Register Notice: Mid-term Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards for Model Year 2022-2025 Light-duty Vehicles (PDF) (38 pp, 452 K, pre-publication, signed April 2, 2018, About PDF) READ MORE
Excerpt from Mid-term Evaluation Final Determination: The Administrator determines that the current standards are based on outdated information, and that more recent information suggests that the current standards may be too stringent. The Administrator thus concludes that the standards are not appropriate in light of the record before EPA and, therefore, should be revised as appropriate. EPA is also withdrawing the previous Final Determination issued by the agency on January 12, 2017, with this notice. EPA, in partnership with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, will initiate a notice and comment rulemaking in a forthcoming Federal Register notice to further consider appropriate standards for model year 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles, as appropriate. On March 22, 2017, EPA published a Federal Register notice providing its intention to reconsider the Final Determination of the Mid-term Evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions standards for model year 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles, this notice was published jointly with the Department of Transportation (DOT). On August 21, 2017, EPA and DOT jointly published a Federal Register notice providing a 45-day public comment period on the reconsideration and EPA held a public hearing on September 6, 2017.
...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION:
I. Introduction
In this notice, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is making a new determination of the Mid-term Evaluation (MTE) of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission standards for model year (MY) 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles. The Administrator determines that the standards are not appropriate in light of the record before EPA, and therefore, should be revised as appropriate. EPA is also withdrawing the January 12, 2017 Final Determination (January 2017 Determination) with this notice. EPA, in partnership with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), will initiate a notice and comment rulemaking in a forthcoming Federal Register notice to further consider appropriate standards for MY 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles, as appropriate.
The Administrator makes this finding due to the significant record that has been developed since the January 2017 Determination. Many of the key assumptions EPA relied upon in its January 2017 Determination, including gas prices and the consumer acceptance of advanced technology vehicles, were optimistic or have significantly changed and thus no longer represent realistic assumptions. For example, fuel price estimates used by EPA in the original rulemaking are very different from recent EIA forecasts. EPA needs to update these estimates in the analysis and more accurately reflect changes in US oil production. Economic inputs such as the social cost of carbon, the rebound effect, and energy security valuation should also be updated to be consistent with the literature and empirical evidence.
EPA has also both developed and received additional data and assessments since the January 2017 Determination regarding technology effectiveness and technology costs which warrant additional consideration.
In making this finding, the Administrator has also considered that the reach and success of the program established in the 2012 rulemaking is significantly limited when consumers cannot afford new cars. New information and data provided show the potential significant negative effects of higher vehicle costs.
Based on our review and analysis of the comments and information submitted, and EPA’s own analysis, the Administrator believes that the current GHG emission standards for MY 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles presents challenges for auto manufacturers due to feasibility and practicability, raises potential concerns related to automobile safety, and results in significant additional costs on consumers, especially low-income consumers. On the whole, the Administrator believes the MY 2022-2025 GHG emission standards are not appropriate and, therefore, should be revised as appropriate. EPA, in partnership with NHTSA, will further explore the appropriate degree and form of changes to the program through a notice and comment rulemaking process. This Determination is not a final agency action. As EPA explained in the 2012 final rule establishing the MTE process, a determination to maintain the current standards would be a final agency action, but a determination that the standards are not appropriate would lead to the initiation of a rulemaking to adopt new standards, and it is the conclusion of that rulemaking that would constitute a final agency action and be judicially reviewable as such.
...
On March 15, 2017, President Trump announced a restoration of the original mid-term review timeline. The President made clear in his remarks, “[i]f the standards threatened auto jobs, then commonsense changes” would be made in order to protect the economic viability of the U.S. automotive industry.”9 In response to the President’s direction, EPA announced in a March 22, 2017, Federal Register notice, its intention to reconsider the Final Determination of the MTE of GHGs emissions standards for MY 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles.10 The Administrator stated that EPA would coordinate its reconsideration with the rulemaking process to be undertaken by NHTSA regarding CAFE standards for cars and light trucks for the same model years.
On August 21, 2017, EPA published a notice in the Federal Register announcing the opening of a 45-day public comment period and inviting stakeholders to submit any additional comments, data, and information they believed were relevant to the Administrator’s reconsideration of the January 2017 Determination.11 EPA held a public hearing in Washington D.C. on September 6, 2017.12 EPA received more than 290,000 comments in response to the August 21, 2017 notice.13
III. The Administrator’s Assessment of Factors Relevant to the Appropriateness of the MY 2022-2025 GHG Emission Standards
In the following sections, the Administrator provides his assessment on why the current standards for MY 2022 – 2025 are not appropriate based on the regulatory provisions found in 40 CFR 86.1818-12(h). The Administrator considered the complete record, including all comments provided on the reconsideration, in his determination.
Factor 1: The availability and effectiveness of technology, and the appropriate lead time for introduction of technology; and Factor 3: The feasibility and practicability of the standards
The Administrator finds, based on the record, including new data and information provided since January 2017, that the January 2017 Determination was optimistic in its assumptions and projections with respect to the availability and effectiveness of technology and the feasibility and practicability of the standards. Accordingly, the Administrator now determines that the MY 2022 – 2025 GHG emissions standards may not be feasible or practicable and there is greater uncertainty as to whether technology will be available to meet the standards on the timetable established in the regulations. This is a result of: (1) the changes in trends of electrification since the January 2017 Determination; (2) reliance on future technology advances; and (3) the acceptance rate of the necessary technology by consumers.
a. The changes in trends of electrification since the January 2017 Determination
The agency’s January 2017 Determination was completed at a time when the trends and data associated with MY 2012 – 2015 showed that the majority of the major car-manufacturing companies were “over-complying” with their relative GHG compliance requirements and building up credits. EPA’s latest data14 alongside new reports and data submitted by stakeholders15 show that starting in MY 2016 many companies, for the first time, had to rely on credits in order to comply with the program, and predicts this will occur again for Model Year 2017. While these companies did remain in compliance, they are relying on banked credits which suggests that it may be increasingly difficult for them to comply going forward as they use up their supply of credits. Additionally, the stringency curve dramatically increases at around the same time these credits could run out, further complicating the feasibility of compliance for MY 2022 – 2025.
The figure below shows that since a peak in 2013, electrified light-vehicle (LV) sales have decreased both as a total and as a percentage of all light-vehicle sales. This calls into question EPA assumptions for the 2012 rulemaking and the January 2017 Determination that sales of electrified LVs will be sufficient to support compliance with the MY 2022 – 2025 standards.
Multiple commenters also questioned the feasibility of the standards due to flagging consumer demand for fuel-efficient vehicles including electric vehicles. The Alliance of Automobile Manufacturers (Alliance) stated that the level of technology modeled by EPA is insufficient to meet the standards and that the actual level of technology needed is misaligned with market realities. Global Automakers similarly charged that “decline in vehicle sales, lower gas prices, an increased preference for light trucks over cars, and sluggish demand for high fuel economy vehicles – are taking place as the stringency of the standards increase at an unprecedented rate. There is, simply put, a misalignment between the increasing stringency of the standards and the decreasing consumer demand for fuel efficiency” and that “revised findings would support the conclusion that adjustments to the regulations are needed.” Global Automakers submitted the figure below to show the sluggish demand for electrification in the U.S. market from 1999 through early 2016.
Figure 1: Figure Submitted by Global Automakers (p. 42) titled: “Figure 16: U.S. Electrified Light Vehicle Sales and Take Rate 1999 - 2016 YTD”
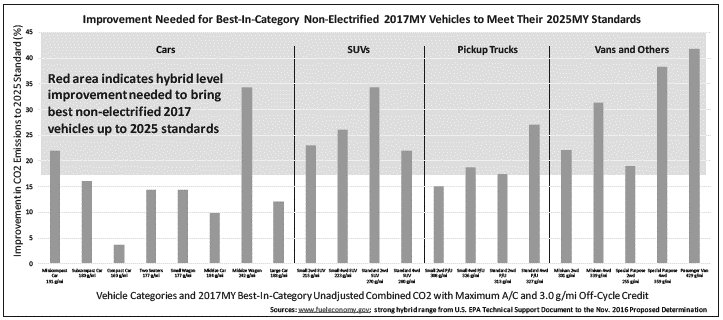
The Alliance stated that “[i]nformation on compliance trends, including the feasibility of meeting the standards, projections on compliance, and the credit system are increasingly indicating that it is not feasible—taking all technology, cost, product cycle, and practical market factors into account—to meet the standards as they are currently set.” For example, Figure 2 below shows that significant vehicle electrification, specifically strong hybrids, would be needed to meet the standards, contrary to the agency’s assertion in the January 2017 Determination.
Figure 2: Figure submitted by the Alliance (p. 18) titled “Figure 5: Improvement in CO2 Emissions Required in the Best MY 2017 Non-Electrified Vehicles to Meet MY 2025 Targets”16
Global Automakers, the Alliance, and individual automakers provided detailed information on a variety of technologies that EPA projected could be used to meet the MY 2022 through 2025 standards.
Regarding the need for electrification, the Alliance asserts that advanced internal combustion engine technologies alone will not meet MY 2025 standards and that the need for greater electrification than EPA originally projected means that issues unique to electrification must be considered. The Alliance further provided that presently only electric vehicles (e.g., strong hybrid, plug-in hybrid (PHEV), or electric vehicle (EV)) meet MY 2025 standards, even with credit assumptions, and that those vehicles make up a minimal amount of the market share indicating a less than adequate acceptance by consumers. Despite automakers continuing to offer an increasing amount of advance technology vehicles for sale, consumer adoption remains very low. These comments provide data that raises concerns about EPA’s 2017 Determination
Toyota provided comment that “compliance with the current requirements through the 2025 MY require gasoline hybrid electric vehicles or more sophisticated forms of vehicle electrification at sales volumes significantly higher than the agencies’ estimates and at levels the market is unable or unwilling to support absent significant changes in market signals.” Toyota further provided that they continue to disagree with EPA’s past assessment that lighter, more aerodynamic vehicles powered by less expensive conventional gasoline powertrains will be sufficient to comply with the standards. Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) similarly indicated, “FCA continues to provide data that shows more technology is necessary than the agencies have assumed for 2022-2025MY compliance. The advanced technologies needed, including higher levels of electrification will negatively affect affordability, lowering sales, and ultimately impacting jobs.” Mercedes Benz estimated that it will need more than 25 percent battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and around 5 percent PHEVs in its fleet to meet the standards in MY 2025, noting that these estimates are significantly higher than the 7 percent BEV and 3 percent PHEV shares projected by EPA for the overall fleet. One commenter stated that they believe standards can be met with only small increases in the efficiency of fossil fuel engines.
EPA also received comments from several non-governmental organizations stating that the existing record supports the previous determination. Several commenters also provided technical information and/or analysis. The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) provided that they do not believe the auto manufacturers are correct about the degree of electrification that they claim will be necessary to meet the standards.
Several commenters supported extending incentives for advanced technologies. The Alliance recommended that EPA extend the advanced technology multiplier incentives beyond MY 2021 and that manufacturers should not be held responsible for upstream power plant emissions (i.e., manufacturers should be allowed to use the 0 g/mile emissions factor for electric powered vehicles rather than having to account for upstream electricity generation emissions). Toyota similarly commented that EPA should extend the current advanced technology sales multiplier and 0 g/mi allowance through MY 2025. Mercedes Benz requested that EPA extend the multipliers through at least MY 2025 to support further commercialization of electric and hybrid vehicles. Jaguar Land Rover supported the reconsideration of the final determination as a way “to enable a future final determination that provides incentives for very clean technologies.”
NGV America urged the agency provide a level playing field for natural gas vehicles. As stated in their comments, “Regulatory incentives currently in place for vehicle manufacturers provide no benefit for renewable natural gas and include requirements that prevent automakers from realizing benefit from selling natural gas vehicles,” including the driving range requirement on alternative fuel that is required for natural gas vehicles but not for electric vehicles.
Several commenters also supported flexibilities for advanced technology vehicles. CALSTART stated that to spur the EV market, the agencies could consider maintaining the current credits for full zero emission vehicles, and delay the upstream emissions factors for such vehicles. Securing America’s Future Energy (SAFE) commented in support of extending the advanced technology credits out to MY 2025 to help facilitate and accelerate the transition to energy sources other than oil. Edison Electric Institute and California Electric Transportation Coalition also commented in support of extending the advanced technology credits. The National Coalition for Advanced Transportation (NCAT) commented that to the extent that EPA seeks to make adjustments to increase flexibility, it urges the agency to recognize and support the role of EVs and other advanced technology vehicles.
The Alliance and Toyota commented that the current full size pick-up truck incentives should be available to all light-duty trucks. They further commented that the program’s sales volume thresholds should be removed because they discourage the application of technology, since manufacturers cannot be confident of achieving the sales thresholds.
Based on consideration of the information provided, the Administrator believes that it would not be practicable to meet the MY 2022 – 2025 emission standards without significant electrification and other advanced vehicle technologies that lack a requisite level of consumer acceptance.
b. Reliance on Future Technology
EPA received comments from the auto manufacturers that EPA should exclude technologies that are protected by intellectual property rights and have not been introduced and certified to Tier 3 emissions requirements. Specifically, the Alliance stated that EPA should exclude from its technology assessments dynamic skip fire, variable compression ratio engines, Mazda’s SkyActiv X, and other technologies that are protected by intellectual property rights and have not been introduced and certified to Tier 3 emissions requirements. Toyota’s information stated that “[n]ot yet implemented technologies, such as advanced cylinder deactivation and 48V mild hybrid systems, can play a role in improving efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions moving forward; however, we do not project these technologies as sufficient to meet the 2025 MY requirements.”
Regarding the use of Atkinson cycle engines, the Alliance commented that the EPA analysis oversimplified and did not consider the financial consequence of aggressive penetration. New information from Global Automakers provided that “it is difficult to maintain confidence in the agency’s optimism about the wide consumer acceptance, supply availability, safety and learning for new, unproven technologies such as the broad application of naturally aspirated Atkinson cycle engines.”
In general, the Alliance, Global Automakers and others found that EPA’s modeling overestimates the role conventional technologies can play in meeting future standards and that industry believes more strong hybrids and plug-in electric vehicles will be needed to meet current standards, raising concerns about cost and affordability. Both the Alliance and Global Automakers submitted detailed information regarding various aspects of EPA modeling, raising several technical issues, and submitted several new studies in support of their comments.17
Other commenters were more optimistic about the availability of advanced technologies. Suppliers provided comments about specific technologies available to meet the standards. The Motor and Equipment Manufacturers Association (MEMA) commented that suppliers continue to improve a myriad of technologies as industry pushes innovation – specifically, more capable 48-volt systems, higher efficiency turbo engines, various advances in thermal management and control technologies, and new composites and materials for improved light-weighting. Manufacturers of Emission Controls Association (MECA) noted that automakers have announced plans to adopt 48-volt mild hybrids at a faster rate than originally planned and commented on new technologies that will be in production prior to 2021 but were not considered in the draft TAR, including dynamic cylinder deactivation, variable compression ratio and electric boost. MECA gave an example that dynamic cylinder deactivation combined with 48-volt systems which they stated has the potential to improve fuel economy by up to 20 percent. One commenter stated that they believe existing standards are achievable now without expensive or “boutique” technologies and are becoming even more cost-effective as time passes.18 Other commenters performed analyses of the technical feasibility of meeting the MY2025 standards,19 including analyses of a number of engine and other technologies that they believe EPA did not fully consider.
Based on EPA’s review of the comments and information received since the January 2017 Determination, technologies continue to develop. Some technologies, such as continuously variable transmissions, have been adopted in many more vehicle applications than originally anticipated by EPA in the 2012 rulemaking and have continued to demonstrate potential further improvements in efficiency. Other technologies such as the dual clutch transmissions EPA projected in the 2012 rulemaking have not gained significant customer acceptance and as such, have proven difficult for manufacturers to deploy. A third category, of recently adopted technologies such as dynamic skip fire (2019 Chevrolet Silverado) and variable compression ratio engines (2019 Infiniti QX50), may have the potential to offer additional technology pathways to aid future compliance. As such, it is appropriate that the EPA continue to evaluate these and other technology developments in the forthcoming rulemaking.
Some commenters supported strengthening the standards in any future reconsideration and at a minimum retaining the standards due to certain new information and analysis available since the rule was adopted in 2012. For example, one commenter stated that they believe the costs of compliance are declining and believes that final compliance costs will be less than initially estimated.
To note, ethanol producers and agricultural organizations commented in support of high octane blends from clean sources as a way to enable GHG reducing technologies such as higher compression ratio engines. They provided information suggesting that mid-level (e.g., E30) high octane ethanol blends should be considered as part of the Mid-term Evaluation and that EPA should consider requiring that mid-level blends be made available at service stations. The petroleum industry noted that high octane fuel is available today for vehicles that require it and commented that EPA has no basis for including octane number as a factor in the Mid-term Evaluation because it was not considered in the prior rulemakings or the draft TAR. The Alliance and Global Automakers commented that higher octane gasoline enables opportunities for use of more energy-efficient technologies (e.g., higher compression ratio engines, improved turbocharging, optimized engine combustion) and that manufacturers would support a transition to higher octane gasoline, but do not advocate any sole pathway for producing increased octane.
Several state and local governments commented on the appropriateness of the MY 2022-2025 standards. CARB referenced its independent midterm review completed in March 2017 where it found the MY 2022-2025 GHG emission standards to be appropriate and that the latest information continues to support maintain or strengthening the current standards.20
Other state government agencies stated that the standards are appropriate, continue to apply, and that they believe compliance will be even easier than expected with newer conventional technologies.
The Aluminum Association provided new studies regarding the use of aluminum in light-weighting and noted additional forthcoming studies which could inform EPA’s reconsideration, commenting that the aluminum industry continues to provide and improve light-weighting solutions to help meet rigorous GHG and fuel efficiency regulations without sacrificing safety.
EPA has given careful consideration to these comments and agrees that these commenters have identified both current and promising technologies that may be able to deliver significant improvements in reducing GHG emissions once fully deployed. However, EPA also recognizes that there is significant uncertainty both in the pace of development of these technologies and in the degree of efficiency improvements they will ultimately be able to deliver. EPA believes that this uncertainty further supports its determination to reconsider the current standards through a subsequent rulemaking.
c. The acceptance of the necessary technologies by consumers
In addition to the issues related to new technologies needing to be developed to meet the MY 2022 – 2025 emission standards, consumers’ preferences must change to ensure that the current standards can be met – that is, consumers will need to be willing to purchase vehicles with new technologies. However, as shown below, consumers’ preferences are not necessarily aligned to meet emission standards and there is uncertainty on this issue that merits further consideration. Consumers’ preferences are driven by many factors and fuel economy is merely one factor that increases and decreases based on the price of gasoline.
The Alliance and Global Automakers state that the standards will be effective only if people buy a mix of vehicles that is sufficiently fuel-efficient on average to meet the standards, but that current trends do not indicate an acceptance by consumers of the increased costs and tradeoffs in other desirable vehicle attributes that are needed to comply with more stringent GHG standards going forward. The only MY 2017 vehicles that could comply with the MY 2025 standard have a very low consumer acceptance rate today and make up less than 5 percent of the total market share (see Figure 2 above). Despite the auto industry providing an increasing number of battery-electric vehicle models and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle models, combined national sales of these vehicles still account for just over one percent of the market. According to data submitted by the Global Automakers, sales of hybrids peaked in 2013 at 3.1 percent, but only accounted for 2 percent of the market in 2016
The Alliance, Global Automakers, Mercedes-Benz, and National Corn Growers Association expressed concerns about low adoption rates of electrified vehicles (strong hybrids, PHEVs, and EVs). Global Automakers stated that customers are not buying electrified vehicles at a rate sufficient for compliance. Mitsubishi and Mercedes-Benz pointed to low gasoline prices and limited infrastructure for electric vehicle charging as an additional obstacle for electric vehicle adoption. Mitsubishi considered the standards unachievable if consumers are not willing to buy more electrification in their vehicles.
Some commenters countered that consumers do prioritize fuel economy that sales numbers decreased because of the cyclical nature of the industry, and that there is enough flexibility in the market to meet consumer needs. Also, a number of commenters asserted that there is a growing understanding and acceptance of electrification in vehicles, pointing to an increased percentage of EV sales and automakers announcing plans for electrification. Contrary to these comments, as shown in Figure 1, EV sales have decreased and when looking at very small numbers, percentage growth may be misleading.
A further issue is the growing preference for light duty trucks over cars. In 2012, the car and light truck shares were projected to be 67 percent to 33 percent respectively for MY 2025. According to EPA’s 2017 Fuel Economy Trends Report, the split in MY 2016 was 55 percent cars and 45 percent trucks. With regard to MY 2016 compliance, the Alliance commented that the large shift in consumer buying patterns toward the light-truck fleet has negatively impacted industry compliance because the light-truck standards were relatively more demanding during this period of time.
Several commenters expressed concern over potential adverse effects on other vehicle attributes due to the standards. The Alliance, Global Automakers, and other stakeholders noted that consumers consider a wide range of features in their purchase decisions. Mercedes-Benz cited low sales of its S550E PHEV which, though more efficient than its internal combustion engine counterpart, had slower acceleration and reduced trunk space. The National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA) and International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW) noted that consumers’ preferences vary with time and market conditions, such as fuel prices. The Alliance, Global Automakers, and Mitsubishi stated that current low gas prices make the standards more difficult to achieve. The Alliance and NADA pointed to a recent study from Resources for the Future that found greater willingness to pay for performance than for fuel economy, and the potential for misestimating willingness to pay if not taking into account other vehicle attributes.21 Global Automakers expressed concern that, if EPA cannot calculate consumers’ willingness to pay for attributes, it may overestimate the probability of success for the standards. One commenter stated that consumers slightly undervalue or fully value future fuel savings while other commenters cited a poll in Ohio supporting achieving an average of 40 mpg in 2025. Consumers Union cited research that found that fuel economy is the top factor that consumers want to be improved in their next vehicle.
Commenters shared perspectives on the current and projected state of the vehicle market and demand. Global Automakers commented that overall vehicle sales have leveled off, and it believes that sales may decline in coming years. CFA noted that vehicle models with larger fuel economy improvements had larger sales increases while sales for those with lower improvements had lower increases. EPA intends to continue to consider vehicle sales and the potential impact of the EPA standards on vehicle sales as a relevant factor in the forthcoming rulemaking.
Various comments raised questions about how to predict the impacts of the standards on vehicle sales. The Alliance and NADA argued that EPA has not yet conducted an “appropriate analysis” of the sales impacts of the standards, and NADA asks the agencies to “fully understand” consumer vehicle purchase decisions. The Alliance referenced work by Ford suggesting that the standards would reduce sales volumes by four percent using cost estimates from the draft TAR. Other commenters provided that neither EPA nor NHTSA has found vehicle demand modeling methods robust enough to predict sales impacts; and EDF stated EPA and NHTSA could consider using a static forecast (that is, assuming market shares to be unaffected by the standards).
Auto industry and dealer comments discussed implications for vehicle fleet turnover. The Alliance noted that low fleet turnover would reduce the effectiveness of the GHG program. NADA suggested that the GHG program should seek to maximize fleet turnover.
Several commenters discussed a study by researchers at Indiana University. The Indiana University’s ‘Total Cost of Ownership’ analysis found that the MY2017-2025 standards would decrease sales using a “2016 perspective” but that it would increase sales when using inputs from the 2012 final rulemaking. Some commenters raised concerns related to the study related to future benefits of improved fuel economy and different assumptions in consumer willingness to pay. Graham, a coauthor of the IU study, supported the assumptions of the report in a response to those comments.
EPA agrees that impacts on new vehicle sales and fleet turnover are important factors that were not adequately considered in the January 2017 Determination. As noted above, if new vehicle sales are lower than expected because of higher prices, or lack of consumer acceptance of advanced technologies, significant share of projected GHG reductions and fuel saving gains on a fleet-wide basis may not be realized. EPA intends to more fully consider these potential actions in the forthcoming rulemaking. EPA intends to explore new analytical tools to look at new vehicle sales and fleet turnover as part of its decision-making record for the new rule.
Factor 2: The cost on the producers or purchasers of new motor vehicles or new motor vehicle engines
The cost on the producers (e.g., suppliers, auto manufacturers), intermediaries (e.g., auto dealers), and purchasers (e.g., consumers, car drivers) can be rather significant based on the standards set. For consumers, especially low-income consumers, moderate increases to the cost of cars can result in significant impacts to disposable income.
Both the Alliance and Global Automakers identified areas where EPA underestimated costs. The Alliance identified three areas related to technology cost that it believes need further assessment: direct technology costs, indirect cost multipliers, and cost learning curves.22 Global Automakers asserted that EPA’s modeling has consistently underestimated the costs associated with technologies and the amount of technology needed, commenting that a quality check at every step of the process needs to be done with real-world data that has been supplied by manufacturers.
The January 2017 Determination did not give appropriate consideration to the effect on low-income consumers. The Administrator believes that affordability of new cars across the income spectrum, and especially among low-income consumers, is an important factor, both because of its equity impacts and because of its potential impacts on the total energy savings delivered by the standards. In its new rulemaking, EPA plans to thoroughly assess the impacts of the standards on affordability and reconsider the importance of this factor in selecting an appropriate level of the standard.
The Alliance, Mitsubishi, and Vermont Energy Investment Corporation (VEIC) recommended that EPA revisit affordability concerns. The Alliance and Global noted that average vehicle transactions prices have increased. The Alliance stated that consumers do not change the fraction of their budgets for transportation; if vehicles become more expensive, they will have to buy less expensive vehicles with fewer features. Global Automakers expected price increases to lead some low-income households to switch from buying new to used vehicles, and some to be forced out of the market entirely. The Alliance reiterated that the standards have a disproportionate negative impact on low-income households.
Mitsubishi expressed concern that it would have to add electrification to already efficient low-priced vehicles and the increased price could drive buyers to less efficient used vehicles. NADA and Graham expressed concerns that potential buyers will not be able to get loans large enough to cover the increased vehicle prices. Mercedes-Benz pointed out that up to half its sales in some markets are leased; the payback period for technologies to meet the standards may exceed the typical three-year leasing period, and low residual values for advanced technologies could further increase lease payments.
The Alliance stated that the standards have a disproportionate negative impact on low-income households. Other commenters stated that the standards will have a larger proportionate benefit for low-income households and referenced a Greene and Welch study23. VEIC requested that the agencies consider that relaxing the standards will increase ownership costs on lower-income drivers. EDF did not find adverse effects on affordability and note that the standards will lead to used vehicle purchasers having more fuel efficient choices.
On the issue of consumer affordability, some stakeholders commented that EPA standards are not making new vehicles less affordable, citing a Synapse Energy Economics report prepared for Consumers Union. The report noted a wider range for vehicle prices at the upper end, due to higher-end vehicles receiving more features, at the same time that the prices of entry-level vehicles have stayed roughly the same for the past 10 years.
EPA concludes that affordability concerns and their impact on new vehicle sales should be more thoroughly assessed, further supporting its determination to initiate a new rulemaking for the 2022-2025 standards.
Factor 4: The impact of the standards on reduction of emissions, oil conservation, energy security, and fuel savings by consumers
The impact of the standards on emissions, oil conservation, energy security, and fuel savings to consumers are significantly affected by many assumptions including but not limited to: (1) the consumer adoption of new lower emitting cars; (2) cost of fuel; and (3) the rebound effects.
Slower or decreased consumer adoption of new lower emitting cars, as mentioned above, would result in decreased effectiveness of the program. As consumer preference changes and/or the cost of new cars increases, consumers may be less willing to purchase new vehicles and thus phase out the higher-emitting older cars. Because of the potential decrease in adoption of newer cars the reduction of emissions from the standards may be less than originally thought. The same logic can be applied to oil conservation. EPA believes that this issue raises enough concern to warrant consideration in the future rulemaking.
With respect to cost of fuel, for example, the lifetime fuel savings to consumers can change by almost 200 percent per vehicle based on the assumption on gas prices according to the 2016 Proposed Determination (Table IV.12). This significant effect on consumer savings due to fuel prices can in turn affect both consumer demand for fuel-efficient vehicles and their driving behavior generally, both of which significantly affect impacts on emissions, oil conservation and energy security. Figure 3 below shows the fuel price projections EPA used in the 2012 final rule, the January 2017 Determination, and the current projections from the Energy Information Administration’s Annual Energy Outlook (AEO). As can be seen from the figure, the 2012 rule projected significantly higher fuel prices than current EIA projections, while the 2017 Final Determination used similar projections to EIA. Lower fuel prices mean lower incentives for consumers to purchase fuel efficient vehicles, because the fuel cost savings they get from doing so are also lower. Thus, the projections for fuel cost savings in the 2012 rule may have been optimistic, which increases the challenge manufacturers face in making fuel-efficient vehicles attractive to consumers. This consideration supports EPA’s determination that the current standards are inappropriate and should be reconsidered in a new rulemaking.
With respect to the rebound effect (the increase in driving resulting from a lower marginal cost of driving due to greater fuel efficiency), EPA received a range of views and assessments in the recent public comments. Higher rebound values mean that consumers are inherently driving more due to the increase in fuel efficiency of the vehicle and this impact will offset the reduction of emissions, oil conservation, energy security, and fuel savings by customers. EPA believes it is important to fully consider the effects of a rebound effect to project an accurate assessment of the projected fuel savings, and EPA intends to do so in its new rulemaking.
With respect to energy security, the situation of the United States is dramatically different than it was at the time the 2012 standards were promulgated, and even significantly different from its situation in 2016 when the draft TAR was developed.
Regarding emissions, some state and local government commenters pointed to the co-benefits of GHG standards as important criteria pollutant control measures. For example, NACAA commented that the standards would lead to oxides of nitrogen (NOx) reduction that contribute to attainment and maintenance of the 2008 and 2015 ozone and 2012 fine particulate matter National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) and other air benefits. While EPA agrees that there are co-benefits from these standards, EPA notes that the standards are supposed to be based on GHG emissions and that while co-benefits exist with respect to emissions such as criteria pollutants, using GHG emission standards as criteria pollutant control measures is likely a less efficient mechanism to decrease criteria pollutants and those issues are already handled through the NAAQS implementation processes.
Based on the information provided above, the Administrator believes that there is strong basis for concern that the current emission standards from MY 2022 – 2025 may not produce the same level of benefits that was projected in the January 2017 Determination. This further supports the Administrator’s determination to withdraw the prior Determination and initiate a rulemaking to reconsider the current standards.
Factor 5: The impact of the standards on the automobile industry
The Administrator finds, based on the current record, that the standards potentially impose unreasonable per vehicle costs resulting in decreased sales and potentially significant impact to both automakers and auto dealers. Trinity Consulting & NERA Economic Consulting (TC/NERA)24 found that the MY 2022-2025 standards would reduce vehicle sales over those four model years from 65 million to 63.7 million, a reduction of 1.3 million vehicles, due to higher vehicle prices.
EPA also recognizes significant unresolved concerns regarding the impact of the current standards on United States auto industry employment. The Center for Automotive Research (CAR),25 a nonprofit automotive research center, developed a cost-benefit study referenced by multiple commenters that estimated employment losses up to 1.13 million due to the standards if the standards increased prices by $6,000 per vehicle. Other stakeholders submitted comments critical of the CAR report.
Commenters expressed differing points of view on the potential effects of the standards on employment and the macroeconomy and predicting the exact effect of the GHG emission standards on the macroeconomy is rather difficult.
Some commenters pointed to negative effects on the economy and employment due to higher costs from the standards. The Alliance commented that each job in the auto sector creates 6.5 additional jobs, and stated that auto sector employment is generally related to vehicle sales, which is expected to decline. The Alliance, Global Automakers, and FCA expressed concern that cost increases associated with the MY 2022-2025 standards could reduce sales and employment, and put downward pressure on the macroeconomy. The Alliance and Global Automakers argued that reduced revenues from a sales drop due to the standards would reduce spending on research and development.
Other commenters stated that the standards could lead to macroeconomic and employment benefits through their effects on innovation. Commenters also stated that innovation and investment resulting from the standards have contributed to the recovery of the auto industry and the wider economy. Some commenters stated that reopening the standards increases uncertainties that may reduce investments in advanced technologies.
The UAW, while not objecting to a reevaluation of the standards, stated that EPA should ensure that the regulations recognize the long-term importance of manufacturing a diverse fleet of motor vehicles in the United States by American workers and radically weakening the standards will adversely impact investments in key technologies and put domestic manufacturers behind in making fuel-saving technologies being used to meet the standards. Some commenters stated they believe there would be positive effects on employment from the standards through their effects on investments.
The automotive supplier commenters discussed their views on the importance of the standards in maintaining the competitive advantage U.S. companies currently have in the global marketplace. For example, MEMA commented that reducing the stringency of the standards in the U.S. increases the likelihood that work on these emissions-reducing technologies would shift to other markets.
A number of commenters cited Carley et al.26, which included a study of the macroeconomic impacts of the standards, conducted by researchers at Indiana University. The study found that the short-term effects of the standards are negative, but the long-term effects of the standards are positive for employment but will not overtake the negative effects until at least 2025. Several commenters identified concerns in the Carley et.al. analysis that contributed to short-term negative effects. Graham, a coauthor of the report, responded to these comments by supporting the IU report assumptions.
EPA finds that a more rigorous analysis of job gains and losses is needed to determine the net effects of alternate levels of the standards on employment and believes this is an important factor to consider in adopting appropriate standards. EPA intends to include such an analysis as part of the basis for the new rule.
Factor 6: The impacts of the standards on automobile safety
EPA and NHTSA considered some potential safety impacts in the 2012 rulemaking, and EPA considers safety to be an important factor in the reconsideration of the MY 2022-2025 standards. For example, fleet turnover is important to an overall safety analysis, as newer cars tend to be safer and more efficient than older cars due to safety technology innovation and regulatory requirements. EPA intends to further assess the scope of its safety analysis in the upcoming rulemaking to examine the possible impacts of fleet turnover on safety. The Administrator finds that this safety analysis is an additional reason to undertake the forthcoming rulemaking.
Factor 7: The impact of the greenhouse gas emission standards on the Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards and a national harmonized program
Many stakeholders commented on the importance of maintaining a National Program for GHG emissions and CAFE standards, and stakeholders urged EPA and NHTSA to continue coordinating with the California Air Resources Board. For example, Global Automakers commented, “Harmonization between the federal and California programs must be maintained. EPA, NHTSA and California need to work together to maintain the One National Program as all parties committed to at its inception.” Toyota commented that its ultimate objective “remains a true, single national standard governing fuel economy and greenhouse gas emissions in the future.” Nissan and Mitsubishi similarly commented that harmonization between federal and California programs must be maintained, urging California, EPA and NHTSA to work together.
Automotive suppliers also commented on the importance of maintaining the National Program. For example, the MEMA stated “[t]he One National Program provides industry stakeholders with economies of scale and increases domestic investment in emissions-reducing and fuel-efficiency technologies and jobs. Anything that falls short of a National Program will fail to provide the long-term planning certainty the industry needs to make the long-term business and technology investment decisions to meet MYs 2022-2025 standards and beyond.” The International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW) commented that all stakeholders should work towards a single National Program and that “California and non-governmental organizations must have a seat at the table along with manufacturers and workers.”
EPA believes that a national harmonized program is very important and will continue to work toward maintaining a national harmonized program through MY 2025 and beyond. To that end, EPA, in collaboration with NHTSA, will initiate a notice and comment rulemaking in a forthcoming Federal Register notice to further consider appropriate standards for MY 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles, as appropriate. This coordination will ensure that GHG emission standards and CAFE standards are as aligned as much as possible given EPA and NHTSA’s different statutory authorities.
EPA and NHTSA have been communicating with stakeholders, including CARB and automobile manufacturers, to try and ensure that a national harmonized program remains intact to minimize unnecessary cost and burdens in the development of the notice and comment rulemaking.
Factor 8: The impact of standards on other relevant factors
The January 2017 Determination also identified regulatory certainty as an additional relevant factor that was considered as part of the determination. EPA understands that automakers and suppliers plan many years in advance.27
Given such long lead times, regulatory certainty can increase the efficiency of business planning and investment cycles. The Administrator agrees that regulatory certainty is extremely important, but is reconsidering its conclusion that maintaining the current standards is the best way to provide such certainty.
Furthermore, industry cannot effectively plan for compliance with the current MY 2022-2025 GHG standards until it knows the outcome of the upcoming NHTSA rulemaking for MY 2022-2025 CAFE standards. Any regulatory certainty potentially provided by the January 2017 Determination is not supported by the fact that NHTSA had not yet begun their statutorily required rulemaking process, and EPA did not know at that time whether NHTSA would establish coordinated requirements. EPA now believes that the greatest potential regulatory certainty is provided in the long run by undertaking a new rulemaking, in partnership with NHTSA, and ensuring that the resulting standards are harmonized to the greatest degree possible.
IV. Revised Determination
Even with the wide range in perspectives, it is clear that many of the key assumptions EPA relied upon in its January 2017 Determination, including gas prices, and the consumer acceptance of advanced technology vehicles, were optimistic or have significantly changed. EPA has also both developed and received additional data and assessments since the January 2017 Determination regarding technology effectiveness and technology costs which warrant additional consideration. In addition, the reach and success of the program is significantly limited when consumers do not purchase new vehicles with low GHG emissions, either because they are priced out of them or are unwilling to spend additional money on advanced fuel-saving technologies.
Based on our review and analysis of the comments and information submitted, the Administrator believes that the current GHG program for MY 2022-2025 vehicles presents difficult challenges for auto manufacturers and adverse impacts on consumers. On the whole, the Administrator believes the MY 2022-2025 GHG emission standards are not appropriate and, therefore, should be revised as appropriate. EPA, in partnership with NHTSA, will further explore the appropriate degree and form of changes to the program through a notice and comment rulemaking process.
As stated above, in this notice, the Administrator has determined that the standards are not appropriate in light of the record before EPA, and therefore, should be revised as appropriate. EPA is also withdrawing the January 2017 Determination with this notice. EPA, in partnership with NHTSA, will initiate a notice and comment rulemaking in a forthcoming Federal Register notice to further consider appropriate standards for MY 2022-2025 light-duty vehicles. This notice concludes EPA’s MTE under 40 CFR 86.1818-12(h). Finally, EPA notes, as discussed above, that this revised determination is not a final agency action, as explained in the 2012 final rule. The effect of this action is rather to initiate a rulemaking process whose outcome will be a final agency action. Until that rulemaking has been completed, the current standards remain in effect and there is no change in the legal rights and obligations of any stakeholders.
1 77 FR 62784, (Federal Register, Vol 77, No 199, pp 62784-62785.)
2 40 CFR 86.1818-12(h).
3 77 FR 62784.
4 40 CFR 86.1818-12(h)(1).
5 Id.; see also 77 FR 62624 (October 15, 2012).
6 81 FR 49217 (July 27, 2016).
7 81 FR 87927 (December 6, 2016).
8 Docket item EPA-HQ-OAR-2015-0827-6270 (EPA-420-R-17-001).
9 See https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefings-statements/remarks-president-trump-american-center-mobility-detroit-mi/.
10 82 FR 14671 (March 22, 2017).
11 82 FR 39551 (August 21, 2017).
12 82 FR 39976 (August 23, 2017).
13 The public comments, public hearing transcript, and other information relevant to the Mid-term Evaluation are available in docket EPA-HQ-OAR-2015-0827.
14 EPA, Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards for Light-Duty Vehicles—Manufacturer Performance Report for the 2016 Model Year, Office of Transportation and Air Quality, EPA-420-R-18-002, January 2018, https://www.epa.gov/regulations-emissions-vehicles-and-engines/greenhouse-gas-ghg-emission-standards-light-duty-vehicles.
15 See e.g., Analysis of EPA Vehicle Technology Walks in Prior Final Determination Response to Comments (Alliance Attachment 2); Evaluation of the Environmental Protection Agency’s Lumped Parameter Model Informed Projections from the Proposed Determination (Novation Analytics, September 2017) (Alliance Attachment 3); and Critical Assessment of Certain Technical and Economic Assumptions Made in EPA’s Final Determination on the Appropriateness of the Model Year 2022-2025 Light-Duty Vehicle Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards under the Midterm Evaluation (Trinity Consultants, NERA Economic Consulting, October 2017) (Alliance Attachment 6).
16 The Alliance submitted this figure in color with the upper shaded portion in red as indicated in the note in the figure.
17 See “Analysis of EPA Vehicle Technology Walks in Prior Final Determination Response to Comments” (Alliance Attachment 2), “Evaluation of the Environmental Protection Agency’s Lumped Parameter Model Informed Projections from the Proposed Determination” (Novation Analytics, September 2017) (Alliance Attachment 3), and “Critical Assessment of Certain Technical and Economic Assumptions Made in EPA’s Final Determination on the Appropriateness of the Model Year 2022-2025 Light-Duty Vehicle Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards under the Midterm Evaluation” (Trinity Consultants, NERA Economic Consulting, October 2017) (Alliance Attachment 6)
18 See comments in the docket from the Advanced Engine Systems Institute
19 See “Efficiency Technology and Cost Assessment for the U.S. 2025-2030 Light-Duty Vehicles” (International Council on Clean Transportation, March 2017, Attachment 5 to ICCT comments), “Technical Assessment of CO2 Emission Reductions for Passenger Vehicles in the Post-2025 Timeframe” (Environmental Defense Fund).
20 CARB, Advanced Clean Cars Midterm Review, Resolution 17-3 (March 24, 2017), available at: https://www.arb.ca.gov/msprog/acc/mtr/res17-3.pdf; CARB, California’s Advanced Clean Cars Midterm Review, Summary Report for the Technical Analysis of the Light Duty Vehicle Standards (January 18, 2017) (p. ES-3), available at: https://www.arb.ca.gov/msprog/acc/mtr/acc_mtr_finalreport_full.pdf. See CARB comments at docket item EPA-HQ-OAR-2015-0827-9197.
21 To note, there are numerous peer-reviewed studies related to this subject and many of them are available in the docket associated with this action. EPA intends to summarize and assess the studies on this topic as part of the forthcoming rulemaking.
22 See “Critical Assessment of Certain Technical and Economic Assumptions Made in EPA’s Final Determination on the Appropriateness of the Model Year 2022-2025 Light-Duty Vehicle Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards under the Midterm Evaluation” (Trinity Consultants, NERA Economic Consulting, October 2017) (Alliance Attachment 6)
23
24 Trinity Consultants & NERA Economic Consulting, Critical Assessment of Certain Technical And
Economic Assumptions Made in EPA’S Final Determination On the Appropriateness of the Model Year
2022-2025 Light-duty Vehicle Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards Under the Midterm Evaluation 2
(Oct. 2017).
25
26 Sanjay Carley, Denvil Duncan, John D. Graham, Saba Siddiki, and Nikolaos Zirogiannis. “A Macroeconomic Study of Federal and State Automotive Regulations,” Indiana University School of Public and Environmental Affairs, March 2017.
27 To note, some commenters raised concerns that reevaluating the standards increases uncertainty that might reduce investment in advanced technologies that could hurt jobs and United States competitiveness. As mentioned below, EPA disagrees with this concern as NHTSA must still complete a rulemaking for MY 2022-2025. READ MORE
Harmonizing a Three-Headed Regulatory Monster (EPA, NHTSA, CARB) (Biofuels Digest)
Opinion: Welch takes on ethanol mandate (Burlington Free Press)
Nearly 55,000 articles in our online library!
Use the categories and tags listed below to access the nearly 50,000 articles indexed on this website.
Advanced Biofuels USA Policy Statements and Handouts!
- For Kids: Carbon Cycle Puzzle Page
- Why Ethanol? Why E85?
- Just A Minute 3-5 Minute Educational Videos
- 30/30 Online Presentations
- “Disappearing” Carbon Tax for Non-Renewable Fuels
- What’s the Difference between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) Diesel? 2020 revision
- How to De-Fossilize Your Fleet: Suggestions for Fleet Managers Working on Sustainability Programs
- New Engine Technologies Could Produce Similar Mileage for All Ethanol Fuel Mixtures
- Action Plan for a Sustainable Advanced Biofuel Economy
- The Interaction of the Clean Air Act, California’s CAA Waiver, Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards, Renewable Fuel Standards and California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard
- Latest Data on Fuel Mileage and GHG Benefits of E30
- What Can I Do?
Donate
DonateARCHIVES
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- June 2009
- May 2009
- April 2009
- March 2009
- February 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- November 2008
- October 2008
- September 2008
- August 2008
- July 2008
- June 2008
- May 2008
- April 2008
- March 2008
- February 2008
- January 2008
- December 2007
- November 2007
- October 2007
- September 2007
- August 2007
- June 2007
- February 2007
- January 2007
- October 2006
- April 2006
- January 2006
- April 2005
- December 2004
- November 2004
- December 1987
CATEGORIES
- About Us
- Advanced Biofuels Call to Action
- Aviation Fuel/Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
- BioChemicals/Renewable Chemicals
- BioRefineries/Renewable Fuel Production
- Business News/Analysis
- Cooking Fuel
- Education
- 30/30 Online Presentations
- Competitions, Contests
- Earth Day 2021
- Earth Day 2022
- Earth Day 2023
- Earth Day 2024
- Earth Day 2025
- Executive Training
- Featured Study Programs
- Instagram TikTok Short Videos
- Internships
- Just a Minute
- K-12 Activities
- Mechanics training
- Online Courses
- Podcasts
- Scholarships/Fellowships
- Teacher Resources
- Technical Training
- Technician Training
- University/College Programs
- Events
- Coming Events
- Completed Events
- More Coming Events
- Requests for Speakers, Presentations, Posters
- Requests for Speakers, Presentations, Posters Completed
- Webinars/Online
- Webinars/Online Completed; often available on-demand
- Federal Agency/Executive Branch
- Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Agriculture (USDA)
- Commerce Department
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Congressional Budget Office
- Defense (DOD)
- Air Force
- Army
- DARPA (Defense Advance Research Projects Agency)
- Defense Logistics Agency
- Marines
- Navy
- Education Department
- Energy (DOE)
- Environmental Protection Agency
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)
- Federal Reserve System
- Federal Trade Commission
- Food and Drug Administration
- General Services Administration
- Government Accountability Office (GAO)
- Health and Human Services (HHS)
- Homeland Security
- Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Interior Department
- International Trade Commission
- Joint Office of Energy and Transportation
- Justice (DOJ)
- Labor Department
- National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- National Research Council
- National Science Foundation
- National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Overseas Private Investment Corporation
- Patent and Trademark Office
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- State Department
- Surface Transportation Board
- Transportation (DOT)
- Federal Aviation Administration
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Admin (PHMSA)
- Treasury Department
- U.S. Trade Representative (USTR)
- White House
- Federal Legislation
- Federal Litigation
- Federal Regulation
- Feedstocks
- Agriculture/Food Processing Residues nonfield crop
- Alcohol/Ethanol/Isobutanol
- Algae/Other Aquatic Organisms/Seaweed
- Atmosphere
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Field/Orchard/Plantation Crops/Residues
- Forestry/Wood/Residues/Waste
- hydrogen
- Manure
- Methane/Biogas
- methanol/bio-/renewable methanol
- Not Agriculture
- RFNBO (Renewable Fuels of Non-Biological Origin)
- Seawater
- Sugars
- water
- Funding/Financing/Investing
- grants
- Green Jobs
- Green Racing
- Health Concerns/Benefits
- Heating Oil/Fuel
- History of Advanced Biofuels
- Infrastructure
- Aggregation
- Biofuels Engine Design
- Biorefinery/Fuel Production Infrastructure
- Carbon Capture/Storage/Use
- certification
- Deliver Dispense
- Farming/Growing
- Precursors/Biointermediates
- Preprocessing
- Pretreatment
- Terminals Transport Pipelines
- International
- Abu Dhabi
- Afghanistan
- Africa
- Albania
- Algeria
- Angola
- Antarctica
- Arctic
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- Asia
- Asia Pacific
- Australia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Barbados
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Belize
- Benin
- Bermuda
- Bhutan
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Botswana
- Brazil
- Brunei
- Bulgaria
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Canary Islands
- Caribbean
- Central African Republic
- Central America
- Chad
- Chile
- China
- Colombia
- Congo
- Congo, Democratic Republic of
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Dominican Republic
- Dubai
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Estonia
- Eswatini/Swaziland
- Ethiopia
- European Union (EU)
- Fiji
- Finland
- France
- French Guiana
- Gabon
- Georgia
- Germany
- Ghana
- Global South
- Greece
- Greenland
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Guinea
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Ivory Coast
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Jersey
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Korea
- Kosovo
- Kuwait
- Laos
- Latin America
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Liberia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mali
- Malta
- Marshall Islands
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mexico
- Middle East
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Mongolia
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Myanmar/Burma
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Netherlands
- New Guinea
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Niger
- Nigeria
- North Africa
- North America
- North Korea
- Northern Ireland
- Norway
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Panama
- Papua New Guinea
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Poland
- Portugal
- Qatar
- Republic of
- Romania
- Russia
- Rwanda
- Saudi Arabia
- Scotland
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Slovakia/Slovak Republic
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South America
- South Korea (Republic of Korea)
- South Sudan
- Southeast Asia
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Timor-Leste
- Togo
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Uganda
- UK (United Kingdom)
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates UAE
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Vatican
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Wales
- Zambia
- Zanzibar
- Zimbabwe
- Marine/Boat Bio and Renewable Fuel/MGO/MDO/SMF
- Marketing/Market Forces and Sales
- Opinions
- Organizations
- Original Writing, Opinions Advanced Biofuels USA
- Policy
- Presentations
- Biofuels Digest Conferences
- DOE Conferences
- Bioeconomy 2017
- Bioenergy2015
- Biomass2008
- Biomass2009
- Biomass2010
- Biomass2011
- Biomass2012
- Biomass2013
- Biomass2014
- DOE Project Peer Review
- Other Conferences/Events
- R & D Focus
- Carbon Capture/Storage/Use
- Co-Products
- Feedstock
- Logistics
- Performance
- Process
- Vehicle/Engine/Motor/Aircraft/Boiler/Ship
- Yeast
- Railroad/Train/Locomotive Fuel
- Resources
- Books Web Sites etc
- Business
- Definition of Advanced Biofuels
- Find Stuff
- Government Resources
- Scientific Resources
- Technical Resources
- Tools/Decision-Making
- Rocket/Missile Fuel
- Sponsors
- States
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawai'i
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Midwest
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Native American tribal nation lands
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- Washington DC
- West Coast
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
- Sustainability
- Uncategorized
- What You Can Do
tags
© 2008-2023 Copyright Advanced BioFuels USA. All Rights reserved.


.jpg)





0 COMMENTS
Leave A Comment
Your Email Address wiil not be Published. Required Field Are marked*