by Patrick O’Brien (Opportune LLP/Biofuels Digest) Find out why knowing the difference between renewable diesel and biodiesel can go a long way in understanding the benefits of each.
Fuel standards programs such as the federal Renewable Fuels Standard (RFS-2) and California’s Low-Carbon Fuels Standard (LCFS) have incentivized fuel producers to innovate and create new renewable fuels like biodiesel and renewable diesel. As new low-carbon diesel fuels and blends become more readily available, it’s important to understand the differences between them and how each impacts engine performance.
Diesel Engine Basics
Before jumping into the different fuel options available, we’ll discuss the basics of a diesel engine and how they differ from gasoline engines. In the U.S., diesel engines are commonly used by trains, boats, barges, and heavy-duty trucks, as well as public buses and farming, construction, and military equipment.
Diesel engines are compression ignition internal combustion engines, ....
...
Diesel engines have the highest thermal efficiency of any internal combustion engine.
...
Biodiesel, or sometimes referred to as fatty acid methyl ester (or FAME), is typically produced by reacting vegetable oils or animal fats with methanol or ethanol in a transesterification process to create mono-alkyl esters of long-chain fatty acids. Biodiesel contains oxygen atoms, which makes it chemically distinct from regular ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD). Like ethanol blending limits in gasoline engines, most diesel engine manufacturers only support diesel blends up to B20, with higher blends requiring fuel system modifications.
Renewable diesel on the other hand uses the same feedstocks as biodiesel; however, it undergoes hydrotreating, thermal conversion, or biomass-to-liquid production processes. The end result is a fungible renewable fuel chemically identical to ULSD that can be used as a drop-in replacement for all current diesel engines.
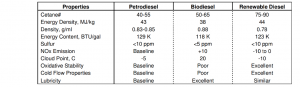
The differences between ULSD, biodiesel, and renewable diesel is best illustrated in the table below, but there are a few properties worth discussion.
(Source: What’s the Difference Between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) Diesel)
Unfortunately, neither renewable diesel nor biodiesel can match the energy density of ULSD. Renewable diesel only has a 4.65% decrease compared to biodiesel’s 8.53% decrease. This value is calculated by multiplying the energy density per unit of mass and the volumetric density and unit conversions. However, the energy density isn’t the only important property related to the energy and volumetric densities. Biodiesel’s higher volumetric density is also responsible for its higher cloud point, poorer cold flow properties, and improved lubricity compared to ULSD. Conversely, renewable diesel’s improved cloud point and cold flow properties can both be attributed to its lower volumetric density.
...
The different chemical properties of the three diesel fuel types significantly impact the resulting GHG, NOx, and particulate matter emissions.
...
Biodiesel decreases almost every emissions category as the percentage blended in ULSD increases, but recent studies have proven it increases NOx emissions compared to ULSD.
...
Based on this information, California’s Air Resource Board (CARB) recently announced a change within their Alternative Diesel Fuels program, which would require biodiesel blends greater than 5% to be approved by CARB. To mitigate this increase in NOx emissions, CARB has approved diesel formulations with at least 55% or 75% renewable diesel and at most 20% biodiesel.
...
While saving only $0.021 per mile may seem insignificant, in 2019 there were 3.91 million Class 8 trucks that drove an average of 62,571 miles.
...
Although renewable diesel has rapidly grown in popularity because it’s a drop-in replacement of ULSD and favorable emissions reductions, some blenders have started to mix the two renewable fuels. REG has created a blend of both biodiesel and renewable diesel, coined “REG Ultra Clean Diesel”, to capture the best attributes of each. Ultra Clean Diesel can reduce emissions across the board while offering improved engine starting, lubrication, reliability, engine life, and more complete combustion.
...
These renewable fuels can reduce lifecycle GHG emissions even more than electric vehicles can since electric vehicles derive their electricity from natural gas, which produces 195% higher GHG emissions on a lifecycle basis than REG B100.
Federal and state governments have realized the potential benefits of biodiesel and renewable diesel and are incentivizing the production of both.
...
Renewable diesel accounts for 1.7 RINs, while biodiesel accounts for 1.5 RINs. READ MORE
What’s the Difference between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) Diesel? 2020 revision (Advanced Biofuels USA)
Breaking down the benefits of biodiesel (National Biodiesel Board; includes VIDEO)
Nearly 55,000 articles in our online library!
Use the categories and tags listed below to access the nearly 50,000 articles indexed on this website.
Advanced Biofuels USA Policy Statements and Handouts!
- For Kids: Carbon Cycle Puzzle Page
- Why Ethanol? Why E85?
- Just A Minute 3-5 Minute Educational Videos
- 30/30 Online Presentations
- “Disappearing” Carbon Tax for Non-Renewable Fuels
- What’s the Difference between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) Diesel? 2020 revision
- How to De-Fossilize Your Fleet: Suggestions for Fleet Managers Working on Sustainability Programs
- New Engine Technologies Could Produce Similar Mileage for All Ethanol Fuel Mixtures
- Action Plan for a Sustainable Advanced Biofuel Economy
- The Interaction of the Clean Air Act, California’s CAA Waiver, Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards, Renewable Fuel Standards and California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard
- Latest Data on Fuel Mileage and GHG Benefits of E30
- What Can I Do?
Donate
DonateARCHIVES
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- June 2009
- May 2009
- April 2009
- March 2009
- February 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- November 2008
- October 2008
- September 2008
- August 2008
- July 2008
- June 2008
- May 2008
- April 2008
- March 2008
- February 2008
- January 2008
- December 2007
- November 2007
- October 2007
- September 2007
- August 2007
- June 2007
- February 2007
- January 2007
- October 2006
- April 2006
- January 2006
- April 2005
- December 2004
- November 2004
- December 1987
CATEGORIES
- About Us
- Advanced Biofuels Call to Action
- Aviation Fuel/Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
- BioChemicals/Renewable Chemicals
- BioRefineries/Renewable Fuel Production
- Business News/Analysis
- Cooking Fuel
- Education
- 30/30 Online Presentations
- Competitions, Contests
- Earth Day 2021
- Earth Day 2022
- Earth Day 2023
- Earth Day 2024
- Earth Day 2025
- Executive Training
- Featured Study Programs
- Instagram TikTok Short Videos
- Internships
- Just a Minute
- K-12 Activities
- Mechanics training
- Online Courses
- Podcasts
- Scholarships/Fellowships
- Teacher Resources
- Technical Training
- Technician Training
- University/College Programs
- Events
- Coming Events
- Completed Events
- More Coming Events
- Requests for Speakers, Presentations, Posters
- Requests for Speakers, Presentations, Posters Completed
- Webinars/Online
- Webinars/Online Completed; often available on-demand
- Federal Agency/Executive Branch
- Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Agriculture (USDA)
- Commerce Department
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Congressional Budget Office
- Defense (DOD)
- Air Force
- Army
- DARPA (Defense Advance Research Projects Agency)
- Defense Logistics Agency
- Marines
- Navy
- Education Department
- Energy (DOE)
- Environmental Protection Agency
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)
- Federal Reserve System
- Federal Trade Commission
- Food and Drug Administration
- General Services Administration
- Government Accountability Office (GAO)
- Health and Human Services (HHS)
- Homeland Security
- Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Interior Department
- International Trade Commission
- Joint Office of Energy and Transportation
- Justice (DOJ)
- Labor Department
- National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- National Research Council
- National Science Foundation
- National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Overseas Private Investment Corporation
- Patent and Trademark Office
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- State Department
- Surface Transportation Board
- Transportation (DOT)
- Federal Aviation Administration
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Admin (PHMSA)
- Treasury Department
- U.S. Trade Representative (USTR)
- White House
- Federal Legislation
- Federal Litigation
- Federal Regulation
- Feedstocks
- Agriculture/Food Processing Residues nonfield crop
- Alcohol/Ethanol/Isobutanol
- Algae/Other Aquatic Organisms/Seaweed
- Atmosphere
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Field/Orchard/Plantation Crops/Residues
- Forestry/Wood/Residues/Waste
- hydrogen
- Manure
- Methane/Biogas
- methanol/bio-/renewable methanol
- Not Agriculture
- RFNBO (Renewable Fuels of Non-Biological Origin)
- Seawater
- Sugars
- water
- Funding/Financing/Investing
- grants
- Green Jobs
- Green Racing
- Health Concerns/Benefits
- Heating Oil/Fuel
- History of Advanced Biofuels
- Infrastructure
- Aggregation
- Biofuels Engine Design
- Biorefinery/Fuel Production Infrastructure
- Carbon Capture/Storage/Use
- certification
- Deliver Dispense
- Farming/Growing
- Precursors/Biointermediates
- Preprocessing
- Pretreatment
- Terminals Transport Pipelines
- International
- Abu Dhabi
- Afghanistan
- Africa
- Albania
- Algeria
- Angola
- Antarctica
- Arctic
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- Asia
- Asia Pacific
- Australia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Barbados
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Belize
- Benin
- Bermuda
- Bhutan
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Botswana
- Brazil
- Brunei
- Bulgaria
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Caribbean
- Central African Republic
- Central America
- Chad
- Chile
- China
- Colombia
- Congo
- Congo, Democratic Republic of
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Dominican Republic
- Dubai
- Ecuador
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eqypt
- Estonia
- Eswatini/Swaziland
- Ethiopia
- European Union (EU)
- Fiji
- Finland
- France
- French Guiana
- Gabon
- Georgia
- Germany
- Ghana
- Global South
- Greece
- Greenland
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Guinea
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Ivory Coast
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Jersey
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Korea
- Kosovo
- Kuwait
- Laos
- Latin America
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Liberia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mali
- Malta
- Marshall Islands
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mexico
- Middle East
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Mongolia
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Myanmar/Burma
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Netherlands
- New Guinea
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Niger
- Nigeria
- North Africa
- North America
- North Korea
- Northern Ireland
- Norway
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Panama
- Papua New Guinea
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Poland
- Portugal
- Qatar
- Republic of
- Romania
- Russia
- Rwanda
- Saudi Arabia
- Scotland
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South America
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Southeast Asia
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Timor-Leste
- Togo
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Uganda
- UK (United Kingdom)
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates UAE
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Vatican
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Wales
- Zambia
- Zanzibar
- Zimbabwe
- Marine/Boat Bio and Renewable Fuel/MGO/MDO/SMF
- Marketing/Market Forces and Sales
- Opinions
- Organizations
- Original Writing, Opinions Advanced Biofuels USA
- Policy
- Presentations
- Biofuels Digest Conferences
- DOE Conferences
- Bioeconomy 2017
- Bioenergy2015
- Biomass2008
- Biomass2009
- Biomass2010
- Biomass2011
- Biomass2012
- Biomass2013
- Biomass2014
- DOE Project Peer Review
- Other Conferences/Events
- R & D Focus
- Carbon Capture/Storage/Use
- Co-Products
- Feedstock
- Logistics
- Performance
- Process
- Vehicle/Engine/Motor/Aircraft/Boiler
- Yeast
- Railroad/Train/Locomotive Fuel
- Resources
- Books Web Sites etc
- Business
- Definition of Advanced Biofuels
- Find Stuff
- Government Resources
- Scientific Resources
- Technical Resources
- Tools/Decision-Making
- Rocket/Missile Fuel
- Sponsors
- States
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawai'i
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Midwest
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Native American tribal nation lands
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- Washington DC
- West Coast
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
- Sustainability
- Uncategorized
- What You Can Do
tags
© 2008-2023 Copyright Advanced BioFuels USA. All Rights reserved.
.jpg)





Comments are closed.